As you work toward completing your ESG reporting, the challenge of collecting accurate data across your entire portfolio can feel overwhelming. With the growing expectations from investors, regulators, and stakeholders, financial organizations like yours are under increasing pressure to provide transparent, reliable ESG reports. Regulatory reporting is crucial in this context, as it ensures that your governance data meets the necessary compliance requirements, thereby enhancing organizational transparency and aiding investment decisions.
From tracking carbon emissions to measuring diversity across your portfolio companies, you need data that is not only accurate but also actionable. To make sure your reporting is comprehensive and meets investor expectations, it’s critical to streamline your data collection process.
In this post, we’ll walk you through five steps that will help you collect ESG data more efficiently, improve data quality, and ensure your reporting drives informed investment decisions.
1. Focus on the most important ESG metrics
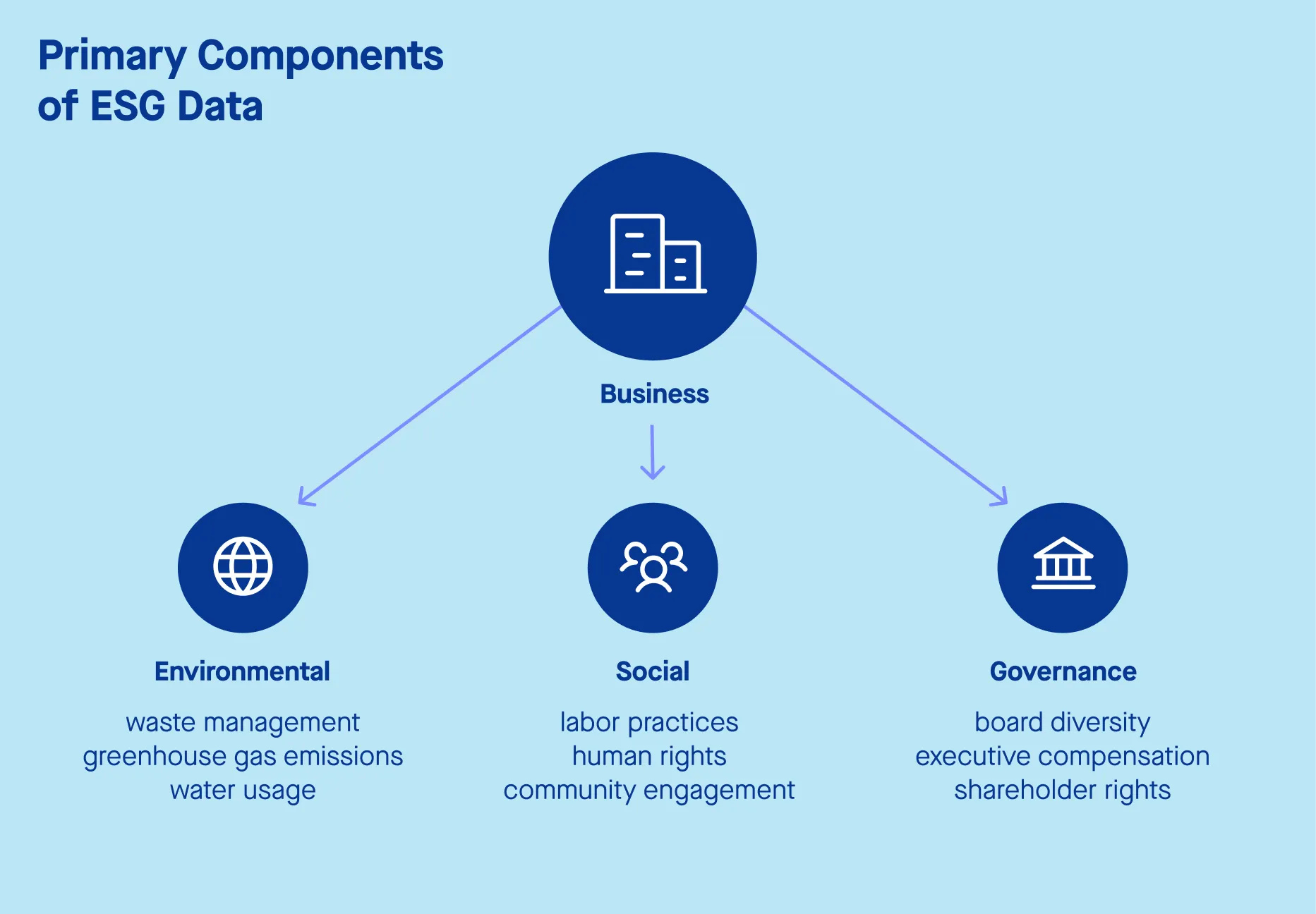
The first step to streamlining your ESG reporting is to focus on the most relevant sustainability metrics. Not all data points are created equal, and it’s essential to prioritize those that have the greatest impact on your portfolio’s performance and your overall ESG goals. For financial organizations, this often means concentrating on metrics such as number of jobs created or % of women on the board across your portfolio companies.
Resist the urge to gather data on every available metric, as this can result in data overload and distract from your core strategic objectives. A more effective method is to perform a double materiality assessment, evaluating both the impact of sustainability issues on your organization and portfolio companies and their relevance to external stakeholders.
Both the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) and the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) incorporate the concept of double materiality. Under SFDR, financial firms must include this information in their pre-contractual and periodic reporting, while portfolio companies are held to the CSRD’s requirements for detailed sustainability disclosures.
In summary, there are two types of ESG data you should aim to gather: data required for regulatory compliance, and data that supports your specific ESG strategy. This strategy may be tailored by sector, shaped by the double materiality of portfolio companies, or focused on commitments made by your investors or your organization.
2. Map your data sources and centralize information
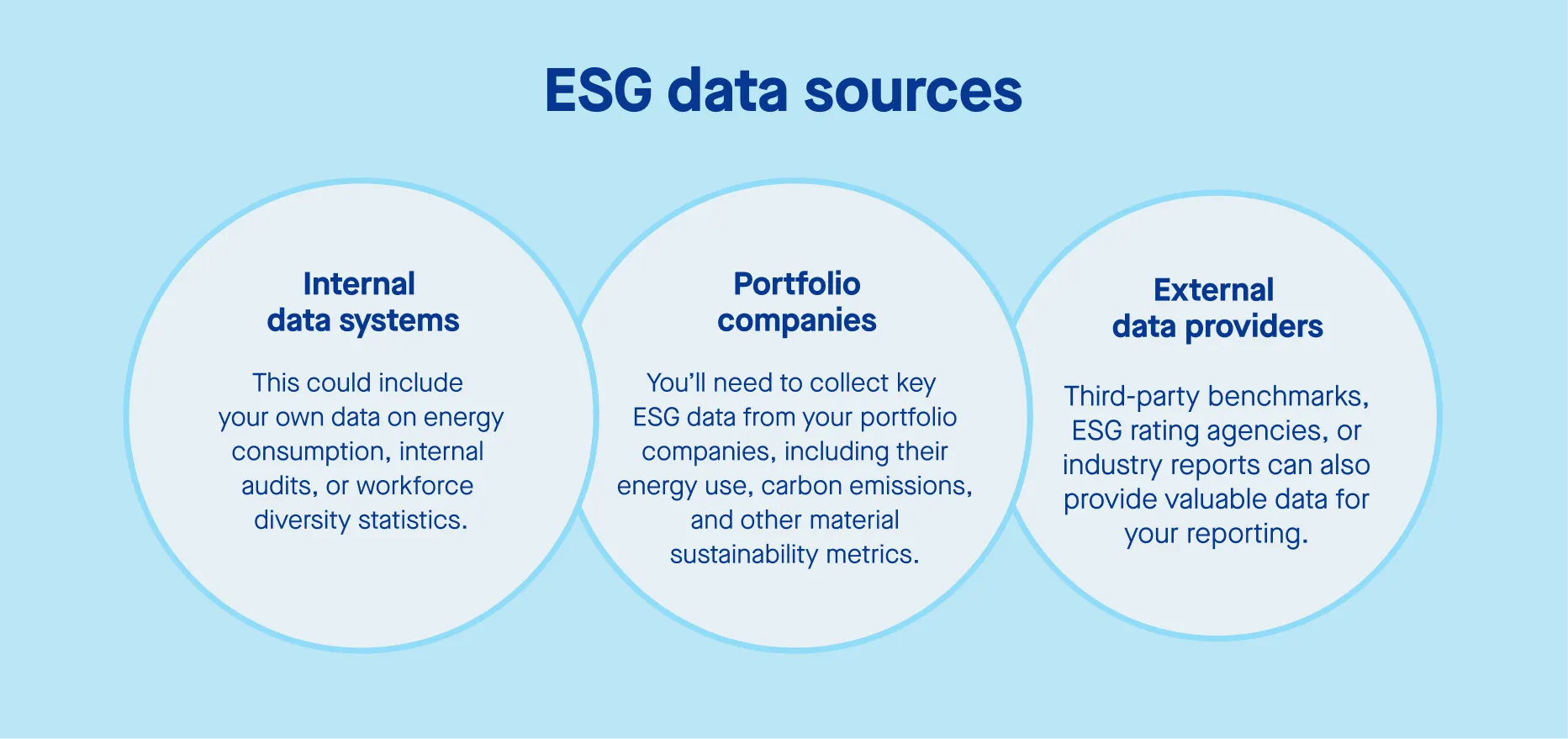
Once you know which ESG metrics to prioritize, the next challenge is figuring out where the data is coming from. Your ESG data is likely scattered across multiple sources—some of it may be internal, while other data may come from investees, third-party benchmarks, or external reports. To streamline your ESG reporting, you’ll need to bring all of these data points together in a centralized system.
Internal data systems
This could include your own data on energy consumption, internal audits, or workforce diversity statistics.
Portfolio companies
You’ll need to collect key ESG data from your portfolio companies, including their energy use, carbon emissions, and other material sustainability metrics.
External data providers
Third-party benchmarks, ESG rating agencies, or industry reports can also provide valuable data for your reporting.
3. Engage your portfolio companies for better data collection
To accurately report on ESG metrics, you’ll need active cooperation from your portfolio companies. For many financial organizations, this can be one of the most challenging parts of the process, as portfolio companies vary in their levels of data maturity and understanding of ESG requirements.
Start by educating your portfolio companies on why ESG data matters—not only for your reporting but for their own sustainability efforts. Help them understand how their carbon emissions, diversity metrics, and other sustainability factors affect your overall ESG and financial performance and why it’s essential to gather accurate, high-quality data.
Providing portfolio companies with clear guidelines on what data to collect and how to collect it will go a long way in streamlining the process. You might also consider sending them tailored surveys that make it easy for them to report on specific ESG metrics like Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions.
Tools that allow for easy data submission, such as automated reporting systems, can help ensure that data collection is both efficient and consistent.
4. Implement strong processes and controls
Ensuring the accuracy and auditability of your ESG data is crucial, particularly in a highly regulated environment. Establishing strong processes and controls will help you manage data quality, track progress, and avoid any gaps or inconsistencies in your reporting.
First, define clear roles and responsibilities for collecting and reviewing ESG data. Each portfolio company should have a designated point of contact who is accountable for providing accurate data. Internally, your team should have a clear process for aggregating, reviewing, and validating the information before it’s used in your ESG reports.
Next, set up a secure, centralized platform for storing your ESG data. This platform should allow you to audit data trails, track changes, and ensure that the data remains reliable over time. Regular quality checks and automated validation tools will help maintain data integrity, ensuring that your reports are based on accurate and comprehensive information.
With these processes in place, you can be confident that your ESG data collection is transparent, reliable, and ready for investor scrutiny.
5. Use your ESG data for informed decision-making
Once you’ve collected and centralized your ESG data, it’s time to put that information to work. The value of ESG reporting goes far beyond compliance; it allows you to make informed decisions about your investment strategy, (highlight the ESG progress made during a company’s detention period) and align your portfolio with your sustainability goals.
For example, analyzing sustainability metrics across your portfolio can help identify areas for improvement. You may discover that certain sectors or companies are disproportionately lowering your ESG KPIs, enabling you to engage them in targeted improvement efforts. Alternatively, ESG data can highlight companies leading in sustainability, presenting opportunities to potentially increase investments in those areas.
Your ESG data will also play a key role in investor disclosures and reporting. By providing transparent, comprehensive ESG reports, you can demonstrate to investors that you are actively managing sustainability risks and opportunities across your portfolio. This transparency builds trust and reinforces your organization’s commitment to long-term value creation.
Final thoughts: Making ESG data collection work for you
As ESG reporting becomes a growing priority for financial organizations, having a streamlined data collection process is essential. By focusing on the right sustainability metrics, centralizing your data, and engaging with your portfolio companies, you can significantly reduce the complexity of ESG reporting. With strong processes in place and the right tools at your disposal, you’ll be well-equipped to provide accurate, transparent ESG reports that meet investor demands and enhance your overall investment strategy.
Whether you’re just starting your ESG journey or looking to refine your data collection processes, following these five steps will help you stay on track and drive long-term value for both your organization and your investors.



