What is the TCFD?
The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) was established in 2015 by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) to create a standardized framework for disclosing climate-related financial risks. The initiative was driven by the growing recognition that climate change is an emerging risk to the global economy and that businesses and financial institutions need to disclose these risks to ensure financial stability.
While the TCFD itself was disbanded in 2023, its framework continues to be widely adopted by businesses, governments, and regulatory bodies.
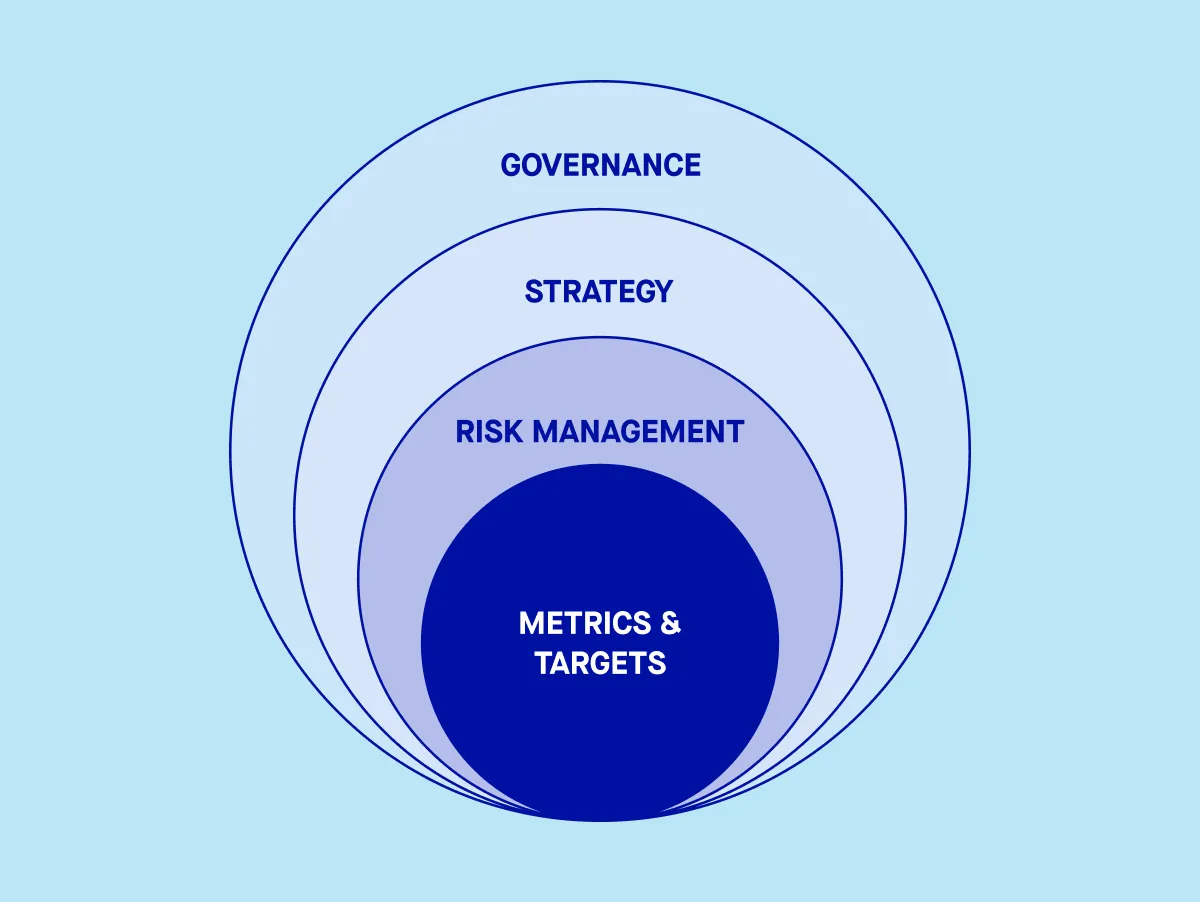
The TCFD framework is built around four core pillars:
- Governance
- Strategy
- Risk Management
- Metrics and Targets
By following these pillars, companies can disclose relevant climate-related risks and opportunities, assess their potential financial impact, and set measurable targets to manage climate-related issues.
What are the benefits of reporting in line with the TCFD?
Adopting TCFD reporting practices brings a host of benefits for businesses, from improving transparency to enhancing long-term sustainability. Here are the key advantages:
Enhanced credibility with investors and stakeholders
Reporting in line with TCFD helps build trust with investors, customers, and stakeholders by demonstrating that the business takes climate-related risks seriously. With climate change becoming a central concern for many stakeholders, companies that align with TCFD show they are actively working toward mitigating these risks and contributing to the global transition to a low-carbon economy.
Improved risk management
Through TCFD reporting, organizations are encouraged to better understand and assess climate-related risks. This proactive approach enables companies to integrate climate considerations into their risk management frameworks and long-term planning. By identifying and addressing climate-related risks early, businesses can mitigate potential negative impacts on their operations, reputation, and financial stability.
Additionally, climate risk disclosures are becoming essential for enhancing transparency and compliance with evolving regulations.
Compliance with regulatory requirements
Governments and regulators in many jurisdictions worldwide are increasingly mandating climate-related disclosures. For example, the European Union’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) requires companies to disclose their climate-related impacts, aligned with TCFD principles. By preparing for TCFD reporting, companies ensure they comply with current and future regulations.
Competitive advantage
By demonstrating transparency and action on climate risks, companies position themselves as leaders in sustainability. This can improve their competitive edge, particularly as consumers and investors increasingly prioritize businesses with strong Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) performance. Companies that implement TCFD reporting can stand out in the marketplace as responsible and forward-thinking organizations.
Better decision-making and long-term planning
TCFD reporting encourages companies to consider the long-term financial implications of climate change. By assessing risks and opportunities across short, medium, and long-term horizons, businesses can make more informed strategic decisions and plan more effectively for the future. This can lead to more resilient business models that are better equipped to handle emerging challenges related to climate change by analyzing the potential impacts on business strategies and financial planning under different climate scenarios.
What are the 11 pillars of the TCFD?
The TCFD framework is structured around four pillars, each with specific recommendations that aim to guide companies in their climate-related disclosures. These pillars are broken down into 11 disclosure recommendations, which organizations should follow when reporting their climate-related risks and opportunities.
Governance
Describe the board’s oversight of climate-related risks and opportunities. Companies should explain how their board of directors is involved in overseeing climate-related risks and opportunities. This includes detailing the responsibilities and processes in place for board members to evaluate climate-related issues.
Describe management’s role in assessing and managing climate-related risks. Companies should outline how management is involved in assessing and managing climate-related risks, including any dedicated roles or teams focused on sustainability and climate issues.
Strategy
Identify the climate-related risks and opportunities over the short, medium, and long term. Organizations should disclose the climate-related risks and opportunities they face across different timeframes. This includes both physical risks (e.g., extreme weather events) and transitional risks (e.g., regulatory changes or shifts in market preferences).
Describe the impact of climate-related risks and opportunities on business, strategy, and financial planning. Companies should outline how climate-related risks and opportunities affect their business strategy, operations, and financial planning. This can include the financial impacts on revenue, costs, and investments, highlighting the need to evaluate and communicate these impacts to stakeholders to assess financial resilience and strategic priorities.
Assess the resilience of the organization’s strategy under different climate-related scenarios. Businesses should assess the resilience of their strategies under different climate-related scenarios, including those that align with a future of global warming of less than 2°C.
Risk Management
Describe the processes for identifying and assessing climate-related risks. Companies should explain how they identify and assess climate-related risks, including the tools and methodologies used to evaluate these risks.
Describe the processes for managing climate-related risks. Organizations need to disclose their approach to managing climate-related risks, including any risk mitigation strategies, contingency plans, and adaptation efforts.
Explain how climate-related risk processes are integrated into the company’s overall risk management. Companies should show how they incorporate climate-related risks into their broader corporate risk management frameworks.
Metrics and Targets
Disclose the metrics used to assess climate-related risks and opportunities. Companies should disclose the metrics they use to measure climate-related risks and opportunities. This includes key performance indicators (KPIs) related to emissions, energy consumption, and resource usage.
Disclose Scope 1, Scope 2, and, if appropriate, Scope 3 greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. TCFD recommends disclosing emissions data across three categories: Scope 1 (direct emissions), Scope 2 (indirect emissions from energy consumption), and Scope 3 (indirect emissions from the supply chain).
Describe the targets used to manage climate-related risks and opportunities. Companies should describe any climate-related targets they have set, such as goals for reducing emissions or transitioning to renewable energy. They should also provide performance data on how well they are meeting these targets.
Identifying Climate Risks
Identifying climate risks is a fundamental step in managing climate-related risks and opportunities. The TCFD emphasizes the importance of assessing both the actual and potential impacts of climate-related risks on an organization’s business, strategy, and financial planning. This involves evaluating physical risks, such as rising sea levels and extreme weather events, which can directly affect operations and assets.
Additionally, organizations must consider transitional risks associated with the shift to a low-carbon economy, including regulatory changes and market dynamics. By analyzing different climate-related scenarios, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of how these risks might impact their financial performance and develop strategies to mitigate them effectively.
Climate-related opportunities represent the potential benefits that organizations can harness from the transition to a low-carbon economy. These opportunities can manifest in various forms, such as the development of innovative products and services, the creation of new markets, and enhancements in operational efficiency.
The TCFD recommends that organizations disclose their climate-related opportunities and outline their strategies for capitalizing on them. This includes setting clear targets and metrics to measure progress and demonstrating how these opportunities align with the organization’s overall strategy for managing climate-related risks and opportunities. By proactively identifying and pursuing climate-related opportunities, businesses can drive growth and sustainability in a rapidly evolving market landscape.
Disclosure Requirements
The TCFD’s disclosure requirements are designed to provide stakeholders with clear, concise, and comparable information on climate-related financial disclosures. Organizations are encouraged to disclose their governance and risk management processes for managing climate-related risks and opportunities. This includes detailing the roles and responsibilities of the board and management in overseeing these risks.
Additionally, companies should outline their strategies for addressing climate-related risks and opportunities, including the metrics and targets used to measure progress. By adhering to these disclosure requirements, businesses can enhance transparency, build trust with stakeholders, and demonstrate their commitment to managing climate-related financial risks effectively.
How can you prepare for reporting?
Preparing for TCFD reporting requires a structured approach to gather data, evaluate risks, and integrate climate considerations into your business processes. Here are key steps companies can take to prepare for reporting:
1. Understand the TCFD framework
Start by familiarizing yourself with the TCFD recommendations and understanding how they apply to your organization. This will provide clarity on what needs to be disclosed and how the framework aligns with your current reporting practices.
Conduct a comprehensive assessment of climate-related risks and opportunities that may affect your business through climate related disclosure. This involves evaluating both physical risks (e.g., extreme weather events) and transitional risks (e.g., regulatory changes or market shifts).
3. Collect data and set targets
Begin collecting the necessary data on your emissions, energy usage, and other climate-related metrics. This will serve as the foundation for your TCFD disclosures. Set measurable targets to reduce emissions, improve energy efficiency, or transition to renewable energy sources.
4. Engage stakeholders
Engage with key stakeholders, including board members, management teams, and external advisors, to ensure alignment on climate-related risks and opportunities. This will ensure that your reporting is accurate and comprehensive.
5. Align with existing reporting standards
If your company already reports in line with other sustainability frameworks, such as GRI or SASB, ensure that your TCFD reporting aligns with these standards. Many companies find it beneficial to integrate TCFD disclosures into their existing sustainability reports.
What are the common challenges?
While TCFD reporting offers significant benefits, many companies face challenges in implementing it. Some common obstacles include:
1. Data availability and quality
Collecting accurate, reliable data on climate-related risks, emissions, and energy usage can be difficult, particularly when dealing with Scope 3 emissions (those that come from the supply chain). Many businesses struggle to obtain comprehensive data from their suppliers.
2. Complexity of scenario analysis
The TCFD recommends that companies assess their resilience under different climate-related scenarios, including those aligned with a 2°C or lower future. Conducting this type of scenario analysis can be complex, as it requires robust models and assumptions. Climate forecasting is essential for TCFD disclosures, despite its imperfections, as it highlights the challenges in accurately estimating the timing and severity of climate events, which are crucial for assessing their potential impacts on businesses, particularly those with complex supply chains.
3. Limited internal expertise
Many companies lack in-house expertise to assess and manage climate-related risks effectively. It can be challenging to find skilled professionals who understand both climate science and financial risk management.
4. Resource constraints
Smaller businesses, in particular, may lack the resources to dedicate to TCFD reporting. This can make it difficult to gather necessary data, conduct risk assessments, and integrate the company’s climate related risks into business strategy.
How can ESG report software help?
ESG reporting software can streamline the process of TCFD reporting by providing businesses with the tools they need to collect, analyze, and report climate-related data using emerging technologies . Here are some key ways ESG software can assist:
1. Centralized data management
ESG software enables businesses to centralize their climate-related data, making it easier to track emissions, energy usage, and other key metrics. This can simplify data collection and ensure consistency across reports.
2. Automation of calculations and reporting
Many ESG reporting platforms offer built-in tools for automatically calculating emissions, energy consumption, and other metrics, which reduces manual work and the risk of errors.
Some ESG platforms come with scenario analysis tools that help businesses model different climate-related scenarios and assess the impact of those scenarios on their operations and financial performance.
These tools are particularly valuable for businesses with complex global supply chains, as assessing risks for these companies involves considering various interconnected and location-specific factors.
4. Integration with existing reporting frameworks
Most ESG software solutions integrate seamlessly with other reporting frameworks, such as GRI, SASB, or CDP, making it easier to combine TCFD disclosures with other sustainability reports.
Integration with existing reporting frameworks
It’s essential to choose ESG software that integrates with major sustainability reporting frameworks—such as the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB), Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), and CDP—to ensure your TCFD disclosures align seamlessly with broader reporting requirements. This integration helps reduce duplication, improve consistency, and save time.
5. Real-time monitoring and progress tracking
ESG platforms provide real-time monitoring capabilities, enabling businesses to track their progress toward climate-related targets and make adjustments as needed.
Best Practices
Implementing the TCFD recommendations effectively requires adopting best practices that integrate climate-related risk management into the organization’s overall risk management framework. This involves ensuring that climate-related risks and opportunities are considered in strategic planning and decision-making processes.
Organizations should also strive to provide climate-related disclosures that are consistent with the TCFD’s recommendations and are updated on a timely basis. Scenario planning is another critical best practice, enabling businesses to assess the potential impacts of different climate-related scenarios on their operations and financial performance.
By following these best practices, organizations can manage their climate-related risks and opportunities more effectively and provide stakeholders with high-quality climate-related financial disclosures.
Ready to start reporting in line with the TCFD?
Adopting TCFD reporting is a crucial step for businesses looking to mitigate climate-related risks, meet regulatory requirements, and enhance transparency. By aligning with TCFD’s recommendations, companies can better prepare for a low-carbon future, drive better decision-making, and improve their competitive advantage.
While there are challenges involved, leveraging ESG reporting software can significantly streamline the process, helping businesses efficiently manage their climate-related disclosures and track their progress.